Starting a Redis Server with a Docker Container
Why Docker Container ?
When using Chocolatey to install Redis in a Windows environment, we often encounter issues with getting the latest version. However, Docker containers running on a Linux environment provide the advantage of working with the most up-to-date Redis systems. Additionally, Docker eliminates the hassle and space allocation required to install a Redis server on a Windows operating system. Instead, it allows us to launch a Redis server effortlessly using a single image.
Starting a Container
To run a Redis server inside a container, we will use the image available at Redis.
In PowerShell, execute the following command:
1
docker run --rm -p 6379:6379 --name rediscontainer -d redis
If the redis image is not available on your Docker platform, it will automatically be pulled from the Docker Hub Registry. Redis, which will be running on port 6379 inside the container, will be accessible externally through port 6373.
Next, let’s run Redis with the command below:
1
docker exec -it rediscontainer redis-cli
As you can see in the image, Redis is now running. Let’s store a message in it:
1
set test "Redis now working"
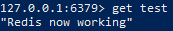
After receiving the “OK” response, let’s retrieve the message:
1
get test
That’s it. As you can see, Redis is working. I hope this is helpful.